
자바는 모든 기본 타입은 값을 갖는 객체를 생성할 수 있음
래퍼 클래스로 감싸고 있는 기본 타입 값은 외부에서 변경할 수 없다.
만약 값을 변경하고 싶다면 새로운 포장 객체를 만들어야 한다.
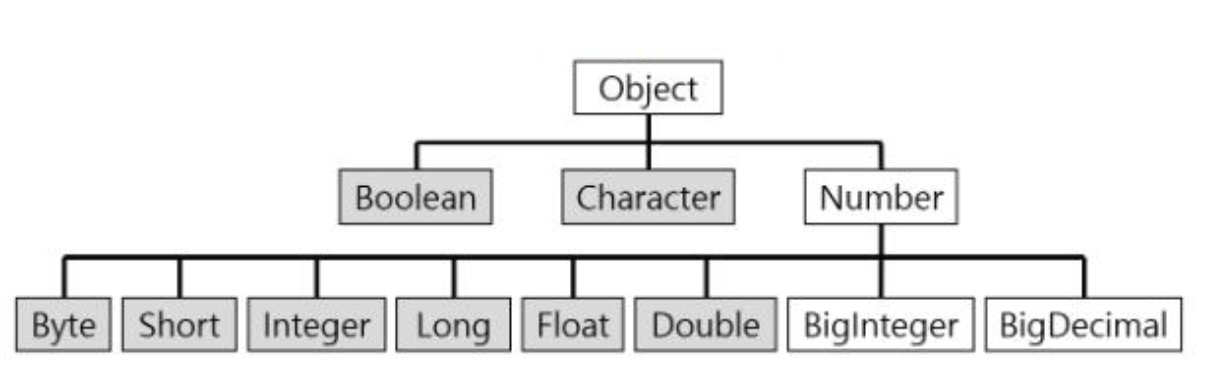
자바에서 Primitive 타입을 객체화 하기 위한 rapper 클래스가 있다.
객체로 만들어 null을 넣거나, 메소드를 사용할 수 있고, toString() 메소드를 사용해 String 타입으로 바로 변환할 수 있음.
List등의 컬렉션에 참조형 타입의 객체를 넣기 위해서 Wrapper 클래스로 한번 감싼것.

Autoboxing : Primitive를 Wrapper Class의 인스턴스로 변환
Autounboxing : 그 반대의 과정
Integer num = 17; // 자동 박싱
int n = num; //자동 언박싱
아래의 코드를 실행하면
Integer num = new Integer(10); //래퍼 클래스1
Integer num2 = new Integer(10); //래퍼 클래스2
int i = 10; //기본타입
System.out.println("래퍼클래스 == 기본타입 : "+(num == i)); //true
System.out.println("래퍼클래스.equals(기본타입) : "+num.equals(i)); //true
System.out.println("래퍼클래스 == 래퍼클래스 : "+(num == num2)); //false
System.out.println("래퍼클래스.equals(래퍼클래스) : "+num.equals(num2)); //true
}
}
결과는 아래와 같다.

래퍼의 객체는 내부의 값을 비교하기 위해 == 연산자를 사용할 수 없다.
왜냐하면 객체의 주소값을 비교하는 것이기 때문이다.
그래서 값을 꺼내서 비교해주는 equals를 통해서 비교해야 한다.
Byte의 equals는 아래와 같이 구현되어 있다.
/**
* Compares this object to the specified object. The result is
* {@code true} if and only if the argument is not
* {@code null} and is a {@code Byte} object that
* contains the same {@code byte} value as this object.
*
* @param obj the object to compare with
* @return {@code true} if the objects are the same;
* {@code false} otherwise.
*/
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof Byte) {
return value == ((Byte)obj).byteValue();
}
return false;
}
래퍼클래스와 기본 자료형의 비교는 ==, equals 연산 모두 가능하다.
왜냐하면 컴파일러가 자동으로 오토언방식을 해주기 때문이다.
valueOf
parse
WrapperCache
Wrapper 클래스 안에 Inner Class가 존재함.
private static class ByteCache {
private ByteCache(){}
static final Byte cache[] = new Byte[-(-128) + 127 + 1];
static {
for(int i = 0; i < cache.length; i++)
cache[i] = new Byte((byte)(i - 128));
}
}
오토박싱을 도와주는 캐시를 가지는 것을 알 수 있다.
기본값은 -128 ~ 127 사이의 값을 가지는 인스턴스를 미리 생성하고 있음.
'개발 > Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Throwable, Exception Class (0) | 2021.05.17 |
|---|---|
| SplitIterator (0) | 2021.05.17 |
| java.util.collections 총정리 List편 (0) | 2021.05.15 |
| java.util.collections 총정리 Queue편 (0) | 2021.05.15 |
| Netty란? (0) | 2021.05.14 |
